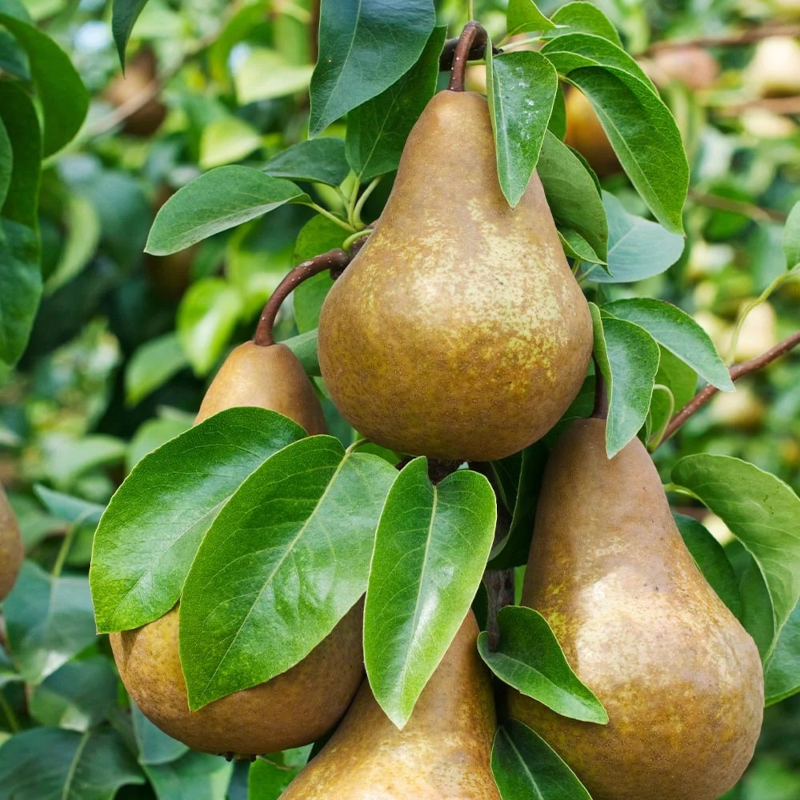
How To
Grow
Pear Tree
Choose the right variety
Select a variety suited to your climate (European or Asian pears).
Check chill hour requirements and disease resistance.
Select a Suitable Location
Choose a sunny spot with well-drained soil.
Ensure good air circulation to reduce disease risk.
Planting
Plant in late winter or early spring while dormant.
Dig a hole twice the width of the root ball and the same depth.
Place the tree in the hole, spread roots, and fill with soil.
Water thoroughly after planting.
Watering and Mulching
Keep the soil evenly moist but not soggy.
Mulch around the base to retain moisture and suppress weeds.
Fertilizing
Fertilize in early spring with a balanced fertilizer.
Avoid over-fertilizing, which may reduce fruit production.
Pruning
Prune in winter to shape the tree and remove dead or diseased branches.
Maintain an open center or central leader structure for good light penetration.
Pollination
Most pear varieties need cross-pollination from another variety nearby.
Plant two compatible varieties within 15–20 meters.
Pest & disease management
Monitor for common issues like fire blight, pear psylla, and codling moth.
Use organic or chemical treatments as needed, and practice good garden hygiene.

Harvesting
Harvest pears when they are mature but still firm; they ripen off the tree.
Check for a slight color change and ease of detachment from the branch.
Health Benefits of Pear
- Supports healthy digestion
- Helps prevent constipation
- May reduce cholesterol levels
- Vitamin C – boosts immunity and acts as an antioxidant
- Vitamin K – supports blood clotting and bone health
- Vitamin B6 – helps with brain and nerve function
- Contains flavonoids and polyphenols
- Protects cells from damage caused by free radicals
- Dietary fiber and antioxidants contribute to heart health
- May help reduce blood pressure and inflammation
- Good for weight management
- Provides a satisfying snack with natural sweetness
- High water content helps maintain hydration
- Low glycemic index fruit
- Does not spike blood sugar rapidly
| Nutrient | Amount / Medium Pear (180Gr) |
| Calories | 101 kcal |
| Water | 84 % |
| Protein | 0.6 g |
| Total Fat | 0.3 g |
| Carbohydrates | 27.1 g |
| – Sugars | 17.4 g |
| – Dietary Fiber | 5.5 g |
| Vitamin C | 7.7 mg (9% DV) |
| Potassium | 206 mg (6% DV) |
| Vitamin K | 8 µg (7% DV) |
| Vitamin B9 | 12 µg (3% DV) |
| Magnesium | 12 mg (3% DV) |
| Copper | 0.1 mg (12% DV) |
| • DV = Daily Value, based on a 2,000-calorie diet. | |
Various Uses of Pear
Fresh Eating
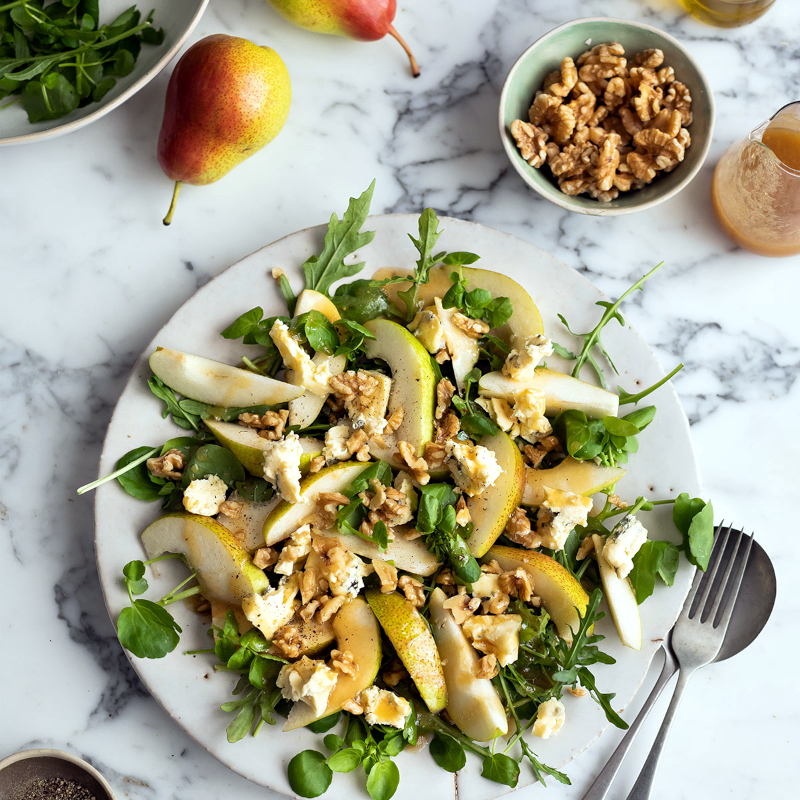

Enjoyed raw as a snack
Added to salads for sweetness and texture
Paired with cheese or nuts for appetizers
Baking
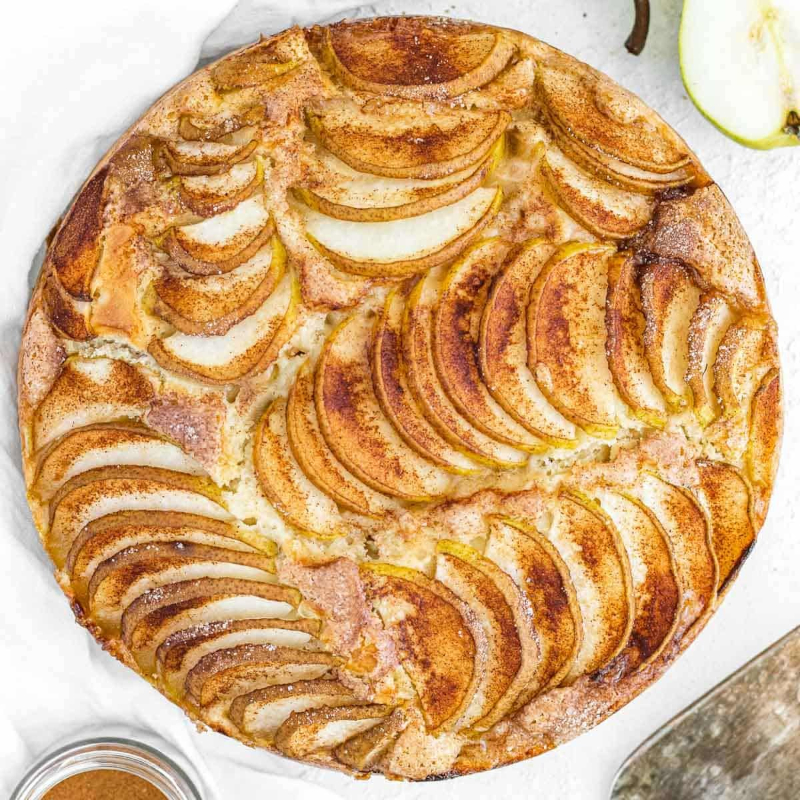

Used in pies, tarts, muffins, cakes, and crumbles
Great for poaching in wine, syrup, or juice with spices
Baked pear halves
Added to upside-down cakes, galettes, and turnovers
Cooking

Roasted or grilled as a side or topping for savory dishes
Stuffed and baked (with nuts, honey, or cheese)
Caramelized in butter and sugar for sauces or toppings
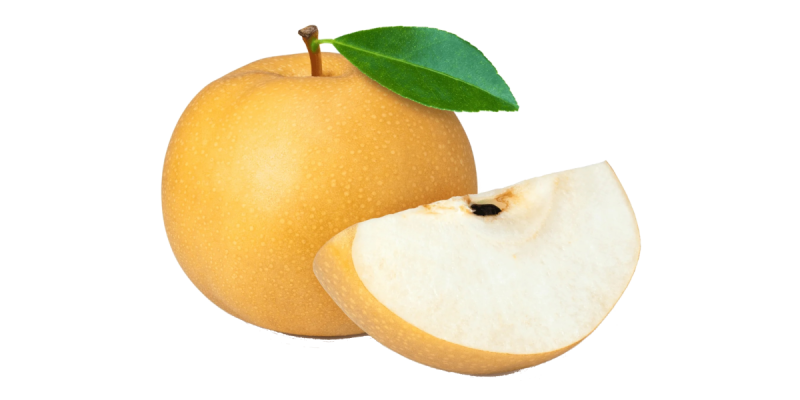
Korean Dishes
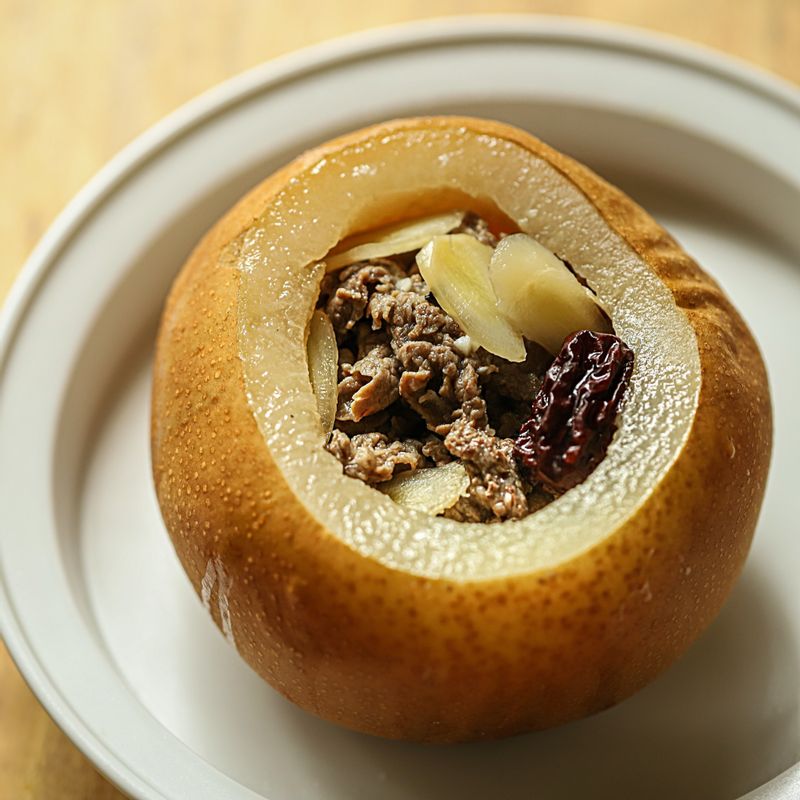

Korean pears are often grated or blended and used in marinades for meats like Bulgogi and Galbi
Touch of sweetness and aids the natural fermentation process
Preservation
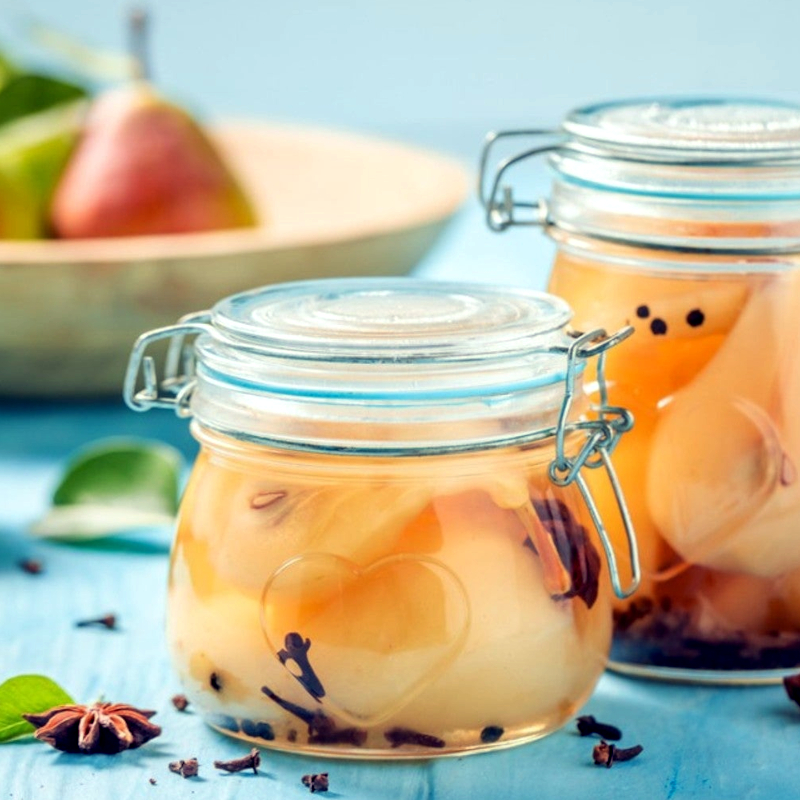

Made into jams, jellies, and preserves
Canned in syrup or juice for long-term storage
Dried as pear chips or slices