Apple

How To
Grow
Apple Tree
Choose the right variety
Select a variety suited to your climate and elevation
Consider disease-resistant types if available
Select a good location
Full sun (at least 6–8 hours of direct sunlight daily)
Well-drained, loamy soil with pH between 6.0 and 7.0
Planting
Plant in early spring or late fall in temperate climates
Dig a hole twice as wide and as deep as the root ball
Place the tree with graft union above the soil line
Fill with soil, water well, and mulch around the base
Watering
Water deeply once or twice a week, depending on weather
Young trees need consistent moisture
Fertilizing
Apply balanced fertilizer in early spring
Avoid over-fertilizing, especially with nitrogen
Pruning
Prune in late winter to shape and remove dead or crossing branches
Encourage open center or central leader form
Pollination
Most apple varieties require a second compatible variety for cross-pollination
Plant at least two varieties nearby or ensure a pollinator is present in the area
Pest & disease management
Monitor for common issues like apple scab, aphids, and codling moth
Use organic or integrated pest management methods if possible

Harvesting
Apples are usually ready 100–200 days after bloom depending on variety
Fruit should be firm, full-colored, and come off easily with a twist
Health Benefits of Apple
- Rich in soluble fiber which helps lower cholesterol
- Contains polyphenols that improve blood vessel function
- High fiber content supports regular bowel movements
- Acts as a prebiotic to nourish good gut bacteria
- Low glycemic index and fiber reduce blood sugar spikes
- Polyphenols may improve insulin sensitivity
- Low in calories and high in fiber
- Promotes satiety and reduces overall calorie intake
- Regular consumption linked with reduced risk
- Antioxidants and fiber contribute to the effect
- Contains vitamin C and phytochemicals
- Helps combat oxidative stress
- Antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds may improve bone density
- Flavonoids may lower risk of lung, colon, and breast cancers
- Apples are about 85 percent water
- Help contribute to daily fluid intake
| Nutrient | Amount / Medium Apple (180Gr) |
| Calories | 95 kcal |
| Water | 156 g |
| Protein | 0.5 g |
| Total Fat | 0.3 g |
| Carbohydrates | 25.1 g |
| – Sugars | 18.9 g |
| – Dietary Fiber | 4.4 g |
| Vitamin C | 8.4 mg (14% DV) |
| Vitamin A | 98 IU (2% DV) |
| Potassium | 195 mg (6% DV) |
| Vitamin K | 4 µg (5% DV) |
| Calcium | 11 mg (1% DV) |
| Iron | 0.2 mg (1% DV) |
| • DV = Daily Value, based on a 2,000-calorie diet. | |
Various Uses of Apple
Eat fresh or raw

Sliced for salads or snacks
Added to yogurt, oatmeal, or cereal
Baking

Apple pies, tarts, and crisps
Apple muffins, cakes, and bread
Cooking
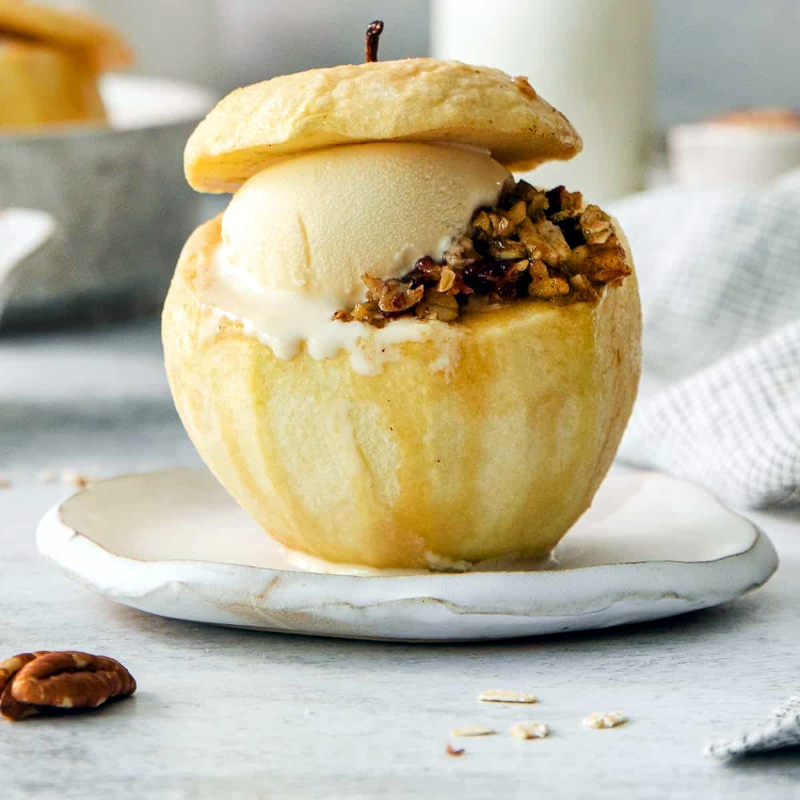

Applesauce as a side or ingredient
Baked apples with spices and nuts
Caramelized apples for pancakes or toast
Savory Dishes
Added to pork, chicken, or duck dishes
Used in stuffings or salads with cheese and nuts
Preservation
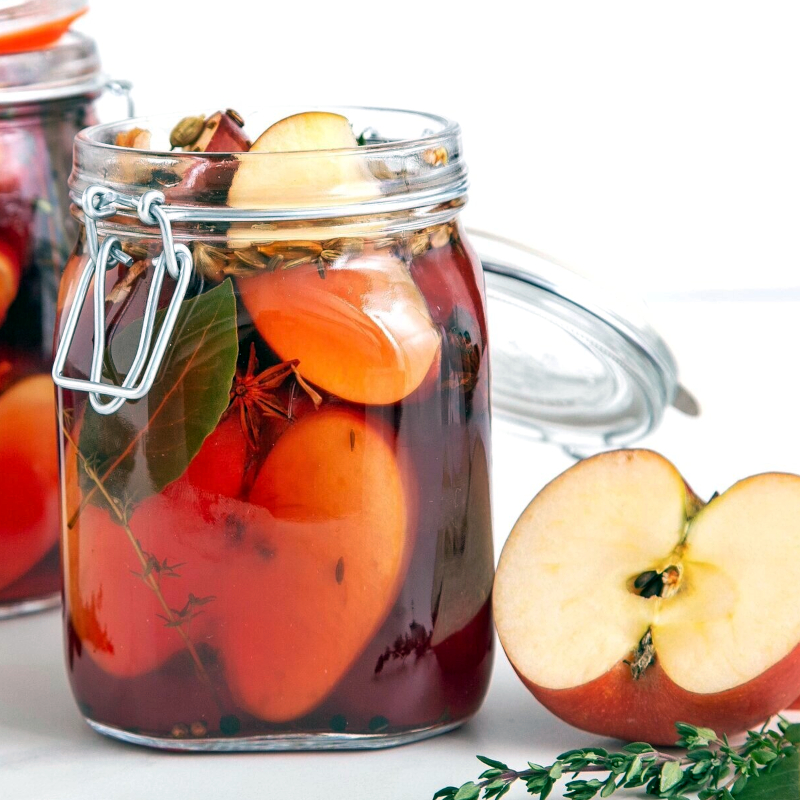

Apple jam or jelly
Apple chutney or butter
Fermented into vinegar or cider









